Stomach pain is a common health complaint that affects individuals of all ages. While it is often temporary and harmless, it can sometimes signal a more serious underlying issue. Understanding the potential causes and available treatments is crucial for effective management.
Common Causes of Stomach Pain
- Indigestion (Dyspepsia):
- Often caused by overeating, spicy foods, or stress.Symptoms include bloating, nausea, and discomfort.

- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):
- Caused by stomach acid flowing back into the esophagus.Symptoms include heartburn, regurgitation, and upper abdominal pain.
- Food Intolerances and Allergies:
- Lactose intolerance and gluten sensitivity are common culprits.Symptoms include cramps, diarrhea, and gas.

- Infections:
- Viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections can lead to stomach pain.Common examples include food poisoning and stomach flu.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS):
- A chronic condition characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, and altered bowel habits.
- Peptic Ulcers:
- Caused by an imbalance between stomach acid and protective mucus.Symptoms include a burning sensation in the upper abdomen.
- Gallstones:
- Hardened deposits in the gallbladder can block bile flow, causing pain.Pain is often severe and located in the upper right abdomen.
- Appendicitis:
- Inflammation of the appendix, requiring immediate medical attention.Symptoms include severe pain in the lower right abdomen, fever, and nausea.

Symptoms to Watch For
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent or severe abdominal pain.
- Pain accompanied by fever, vomiting, or diarrhea.
- Blood in stools or vomit.
- Sudden, sharp pain in the lower abdomen.

Treatment Methods
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoid trigger foods and eat smaller, frequent meals.Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.

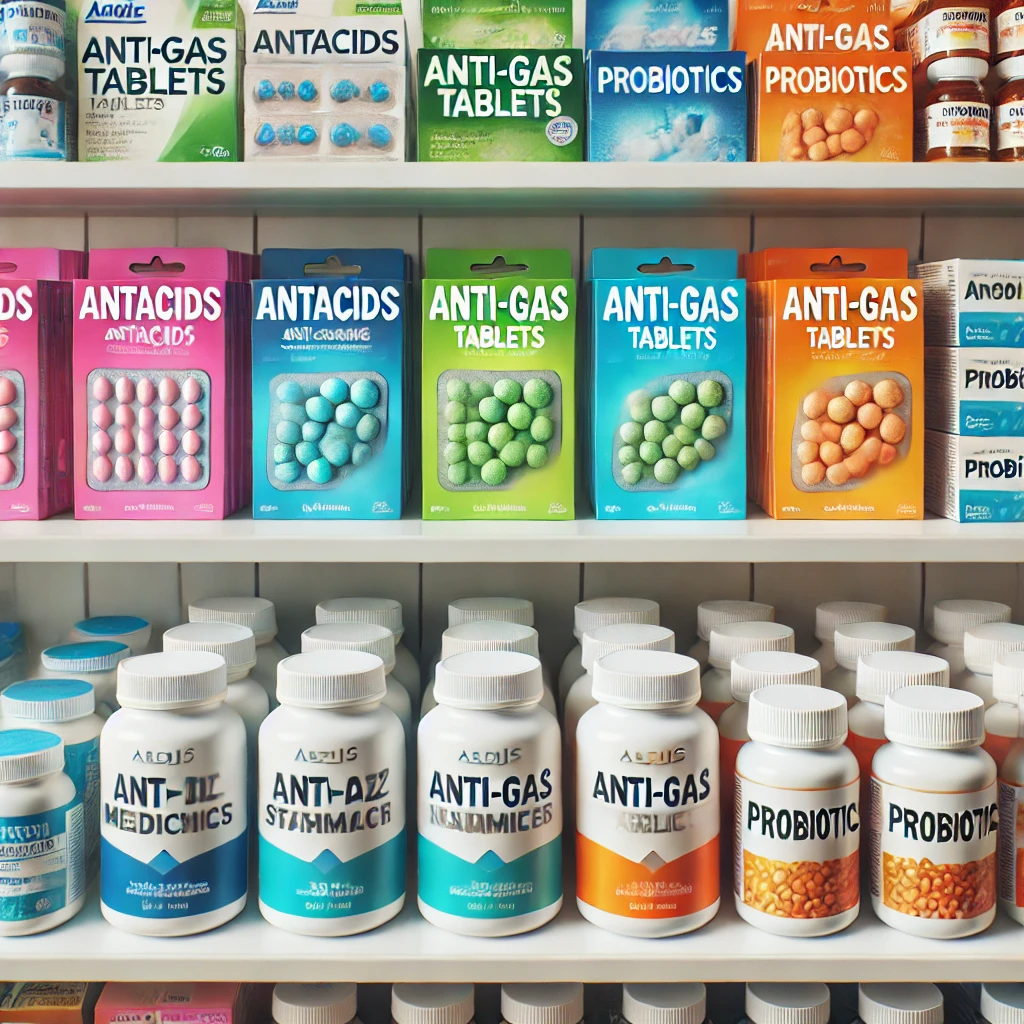
- Over-the-Counter Medications:
- Antacids for heartburn and indigestion.Anti-gas medications for bloating and discomfort.

- Prescription Medications:
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) for GERD.Antibiotics for bacterial infections.Antispasmodics for IBS.

- Home Remedies:
- Ginger tea or peppermint oil for nausea.Warm compress for mild cramps.

- Medical Procedures:
- Endoscopy for diagnosing ulcers or GERD.Surgery for conditions like appendicitis or gallstones.
Prevention Tips
- Healthy Diet:
- Focus on high-fiber foods and stay hydrated.
- Regular Exercise:
- Promotes digestion and reduces stress.

- Avoid Harmful Habits:
- Limit alcohol and avoid smoking.
- Routine Check-Ups:
- Regular medical visits for early detection of issues.

Conclusion
Stomach pain can stem from various causes, ranging from benign to serious. By recognizing symptoms and understanding treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health. When in doubt, consulting a healthcare provider ensures the best outcomes.


