Sleeplessness, or insomnia, is a pervasive issue affecting millions of Americans. Understanding its causes and exploring treatment methods can help individuals reclaim restful nights and improve their overall quality of life.
Common Causes of Sleeplessness
- Stress and Anxiety:
- Worries about work, finances, or personal issues can keep the mind active, making it difficult to fall asleep.
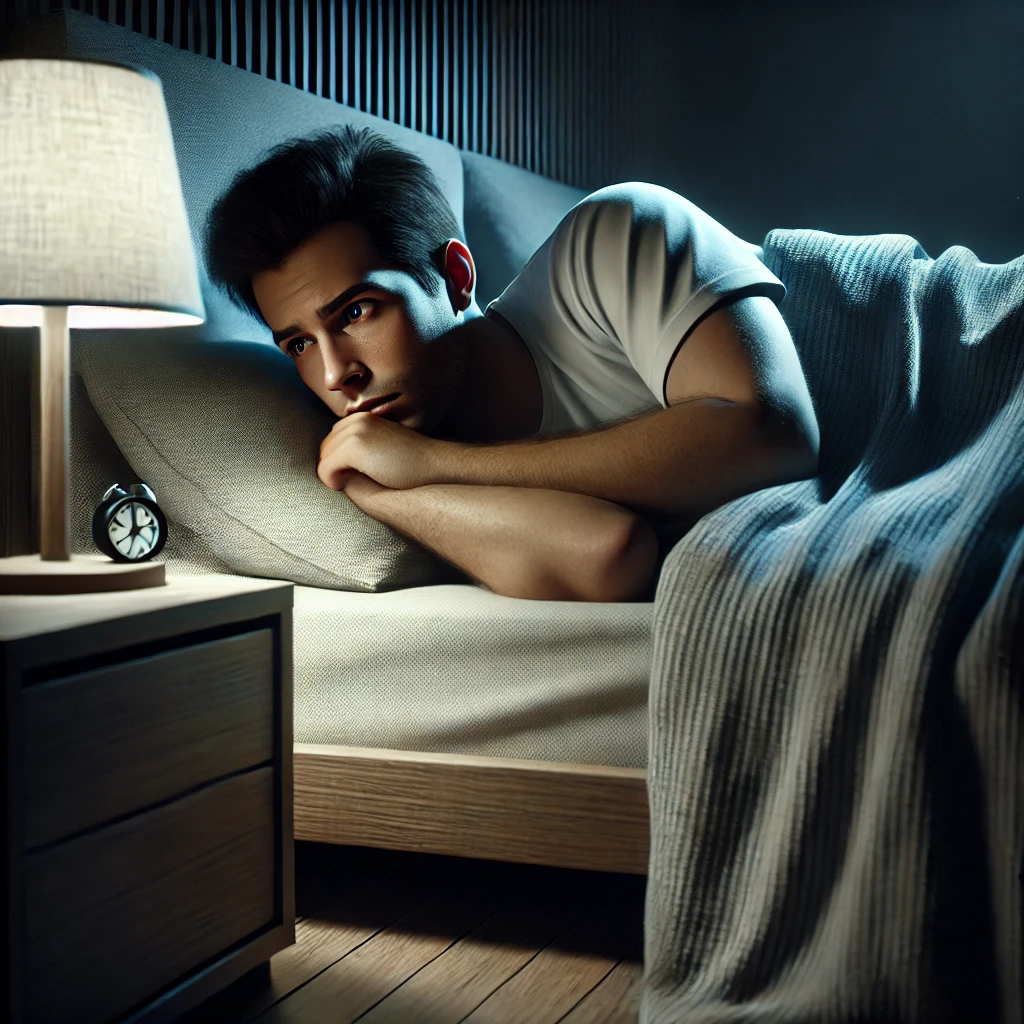

- Poor Sleep Hygiene:
- Irregular sleep schedules, excessive screen time before bed, and a disruptive sleep environment can contribute to sleeplessness.
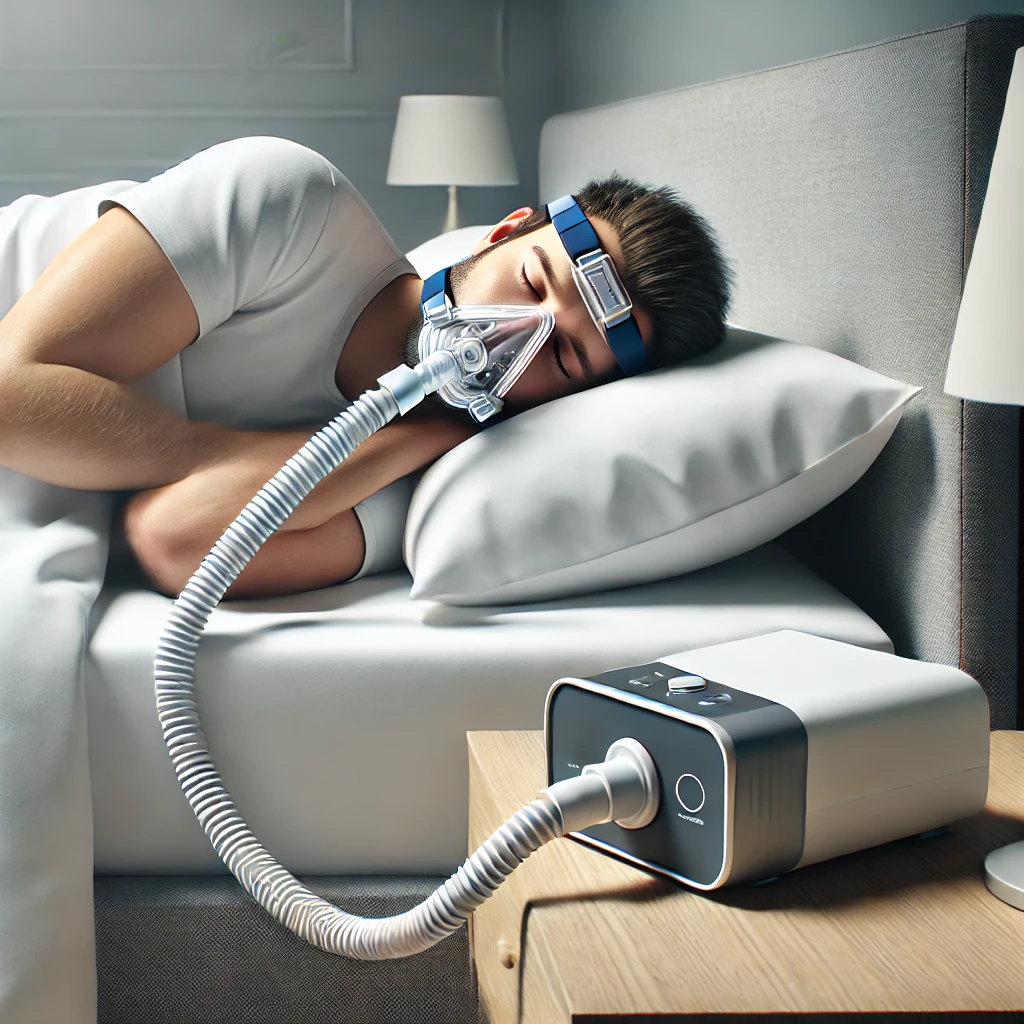
- Medical Conditions:
- Chronic pain, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and other health issues can interfere with restful sleep.

- Dietary and Lifestyle Factors:
- Consuming caffeine, alcohol, or heavy meals close to bedtime can disrupt sleep patterns.

- Mental Health Disorders:
- Depression, PTSD, and other mental health conditions often go hand-in-hand with insomnia.

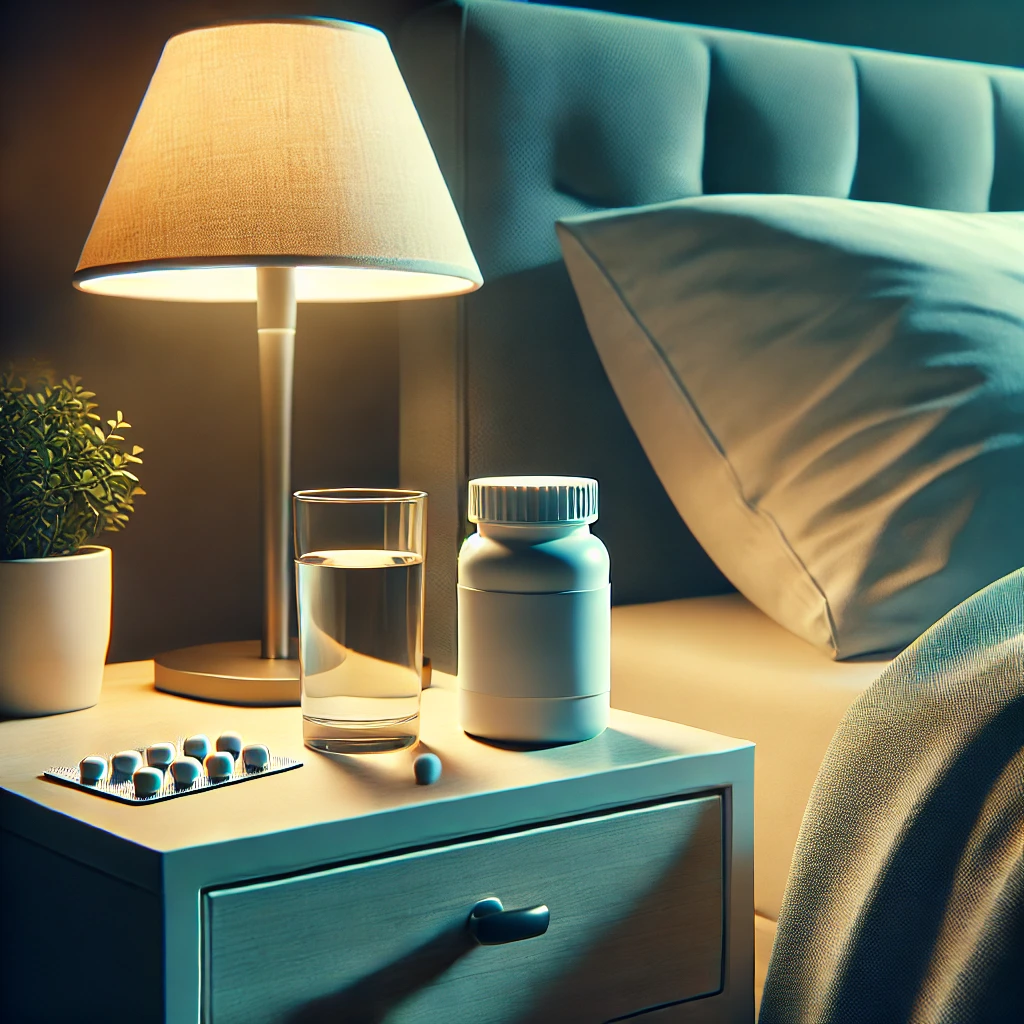
- Medications and Substances:
- Certain prescription drugs and recreational substances can have side effects that disrupt sleep.

Symptoms of Sleeplessness
- Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
- Waking up too early and being unable to fall back asleep.
- Feeling tired or unrefreshed upon waking.
- Irritability, lack of focus, and reduced productivity during the day.

Treatment Methods
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practice meditation, deep breathing, or progressive muscle relaxation.
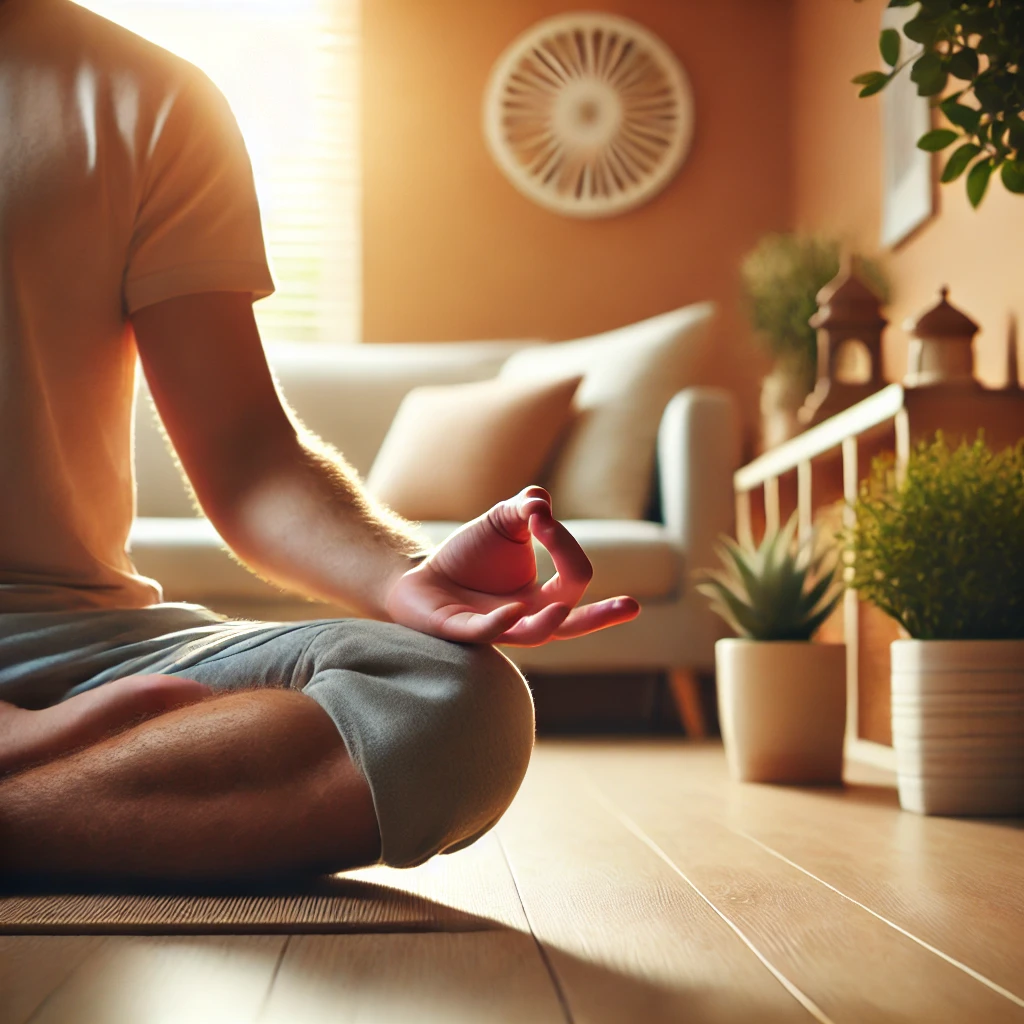

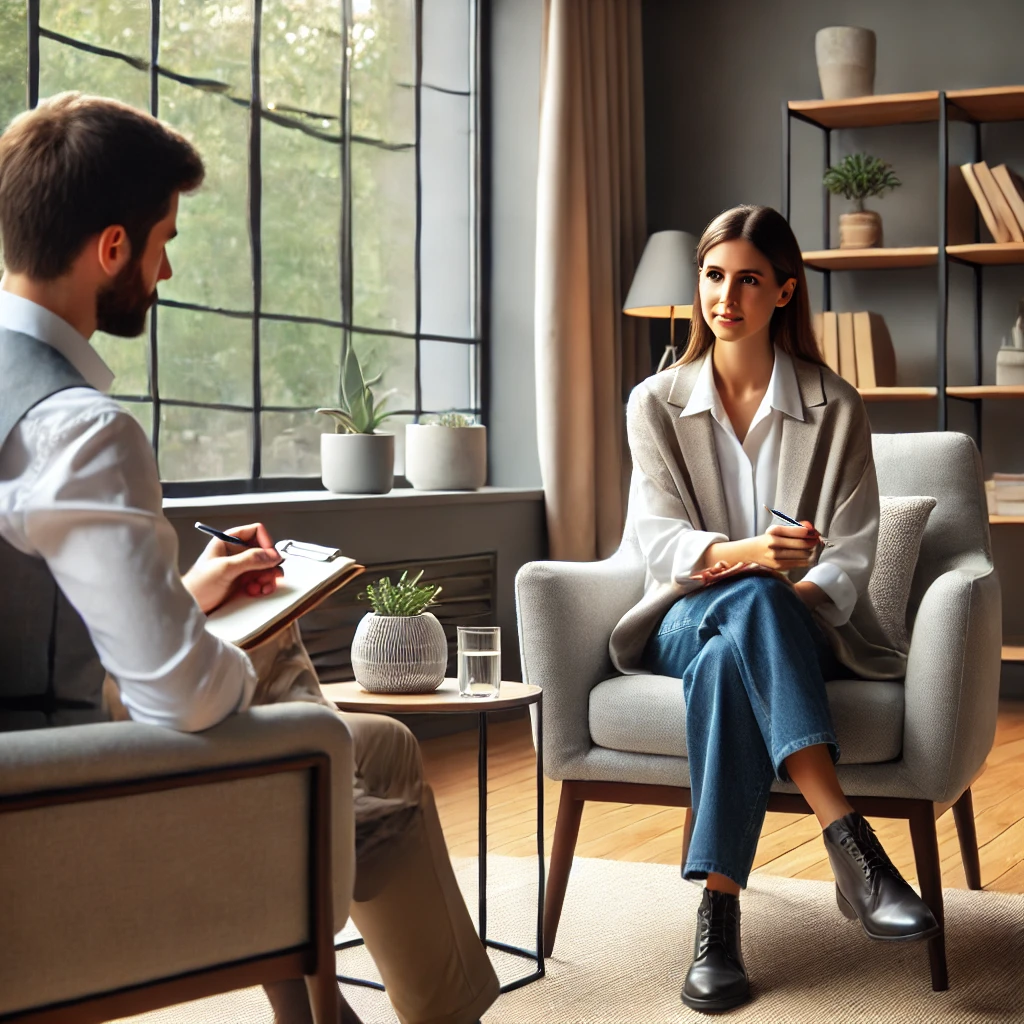
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I):
- A structured, evidence-based approach to identify and change sleep-disruptive thoughts and behaviors.

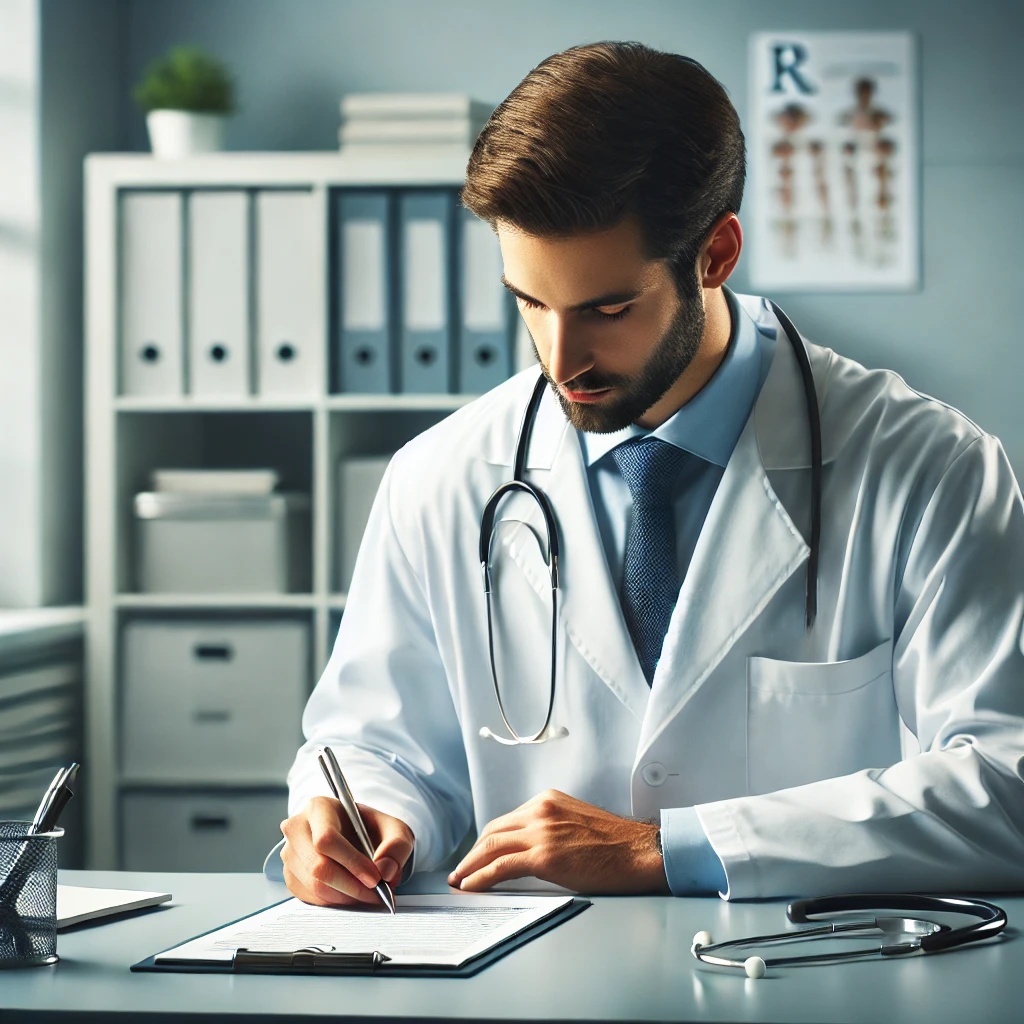
- Medications:
- Prescription sleep aids may be used for short-term relief but are not a long-term solution.

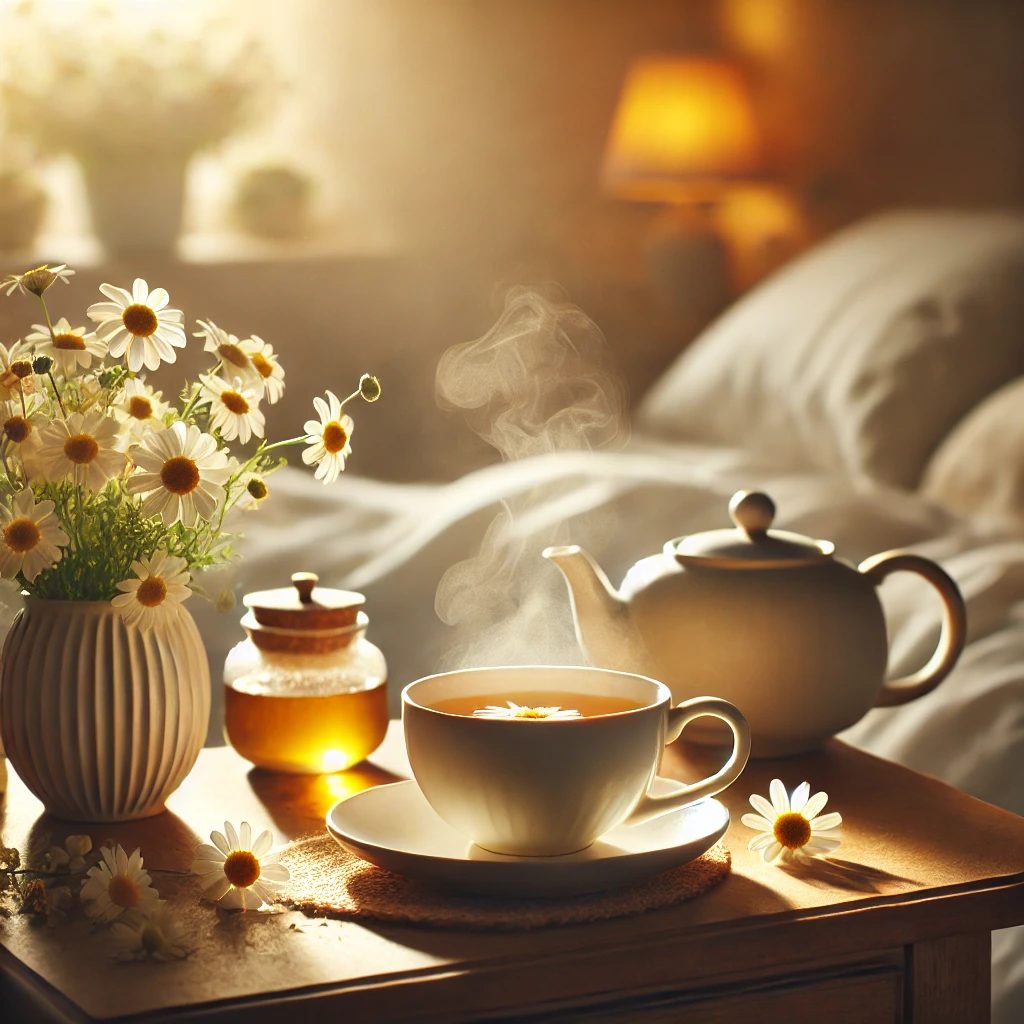
- Natural Remedies:
- Herbal teas like chamomile or supplements like melatonin can promote relaxation.

- Sleep Studies:
- For persistent issues, a sleep study can help diagnose underlying conditions like sleep apnea.

Prevention Tips
- Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment:
- Keep the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet.
- Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows.

- Limit Screen Time Before Bed:
- Reduce exposure to blue light from devices at least an hour before bedtime.

- Regular Exercise:
- Engaging in physical activity during the day can promote better sleep at night.

- Healthy Diet:
- Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime.

When to Seek Help
- If sleeplessness persists for more than three weeks.
- When insomnia interferes with daily activities or mental health.
- If you suspect an underlying medical condition like sleep apnea.

Conclusion
Sleeplessness can significantly impact one’s physical and mental well-being, but it is a manageable condition. By identifying the root causes and adopting effective treatments, individuals can achieve restful, rejuvenating sleep. If you are struggling with persistent insomnia, consult a healthcare provider to explore tailored solutions.


