Acne is a prevalent skin condition that affects millions of individuals across the United States. While it’s often associated with adolescence, people of all ages can experience acne. Understanding its causes and exploring effective treatment methods can help manage and prevent this common dermatological issue.
Understanding Acne
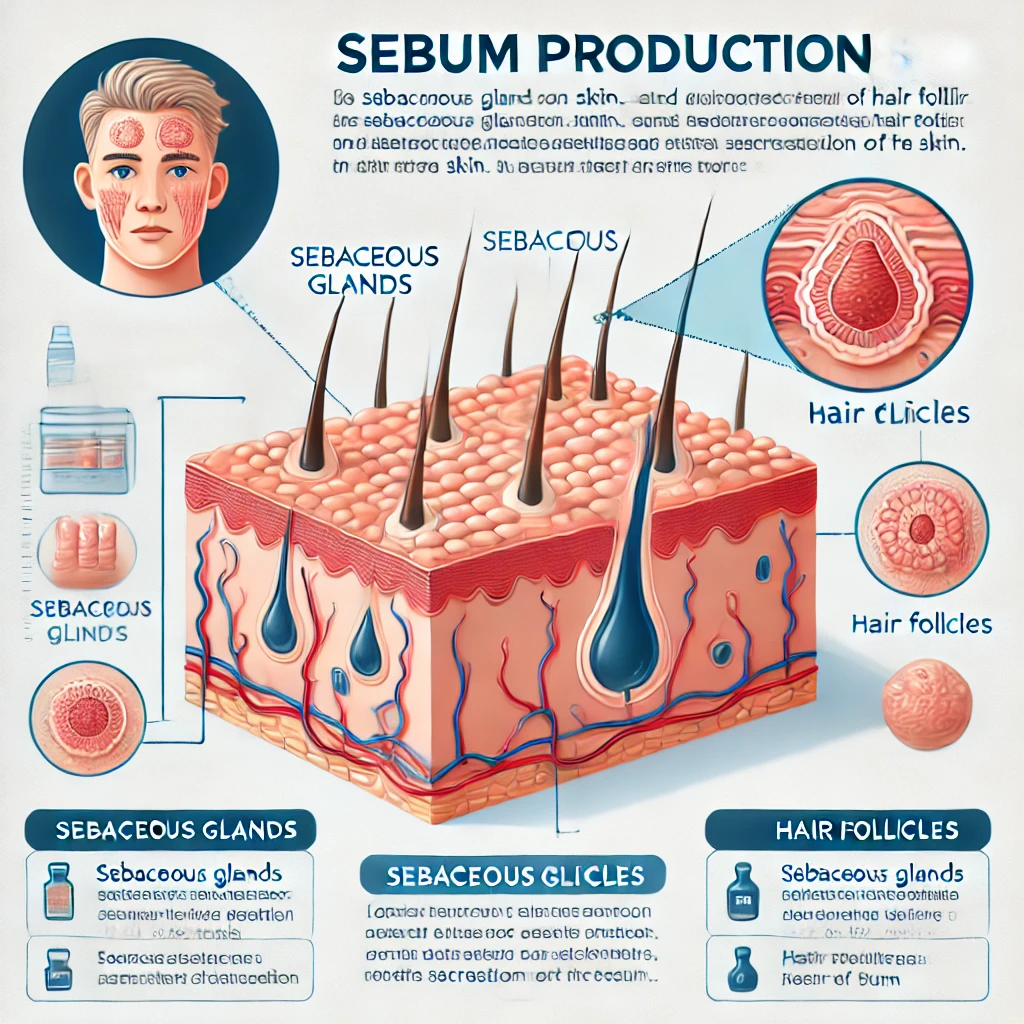
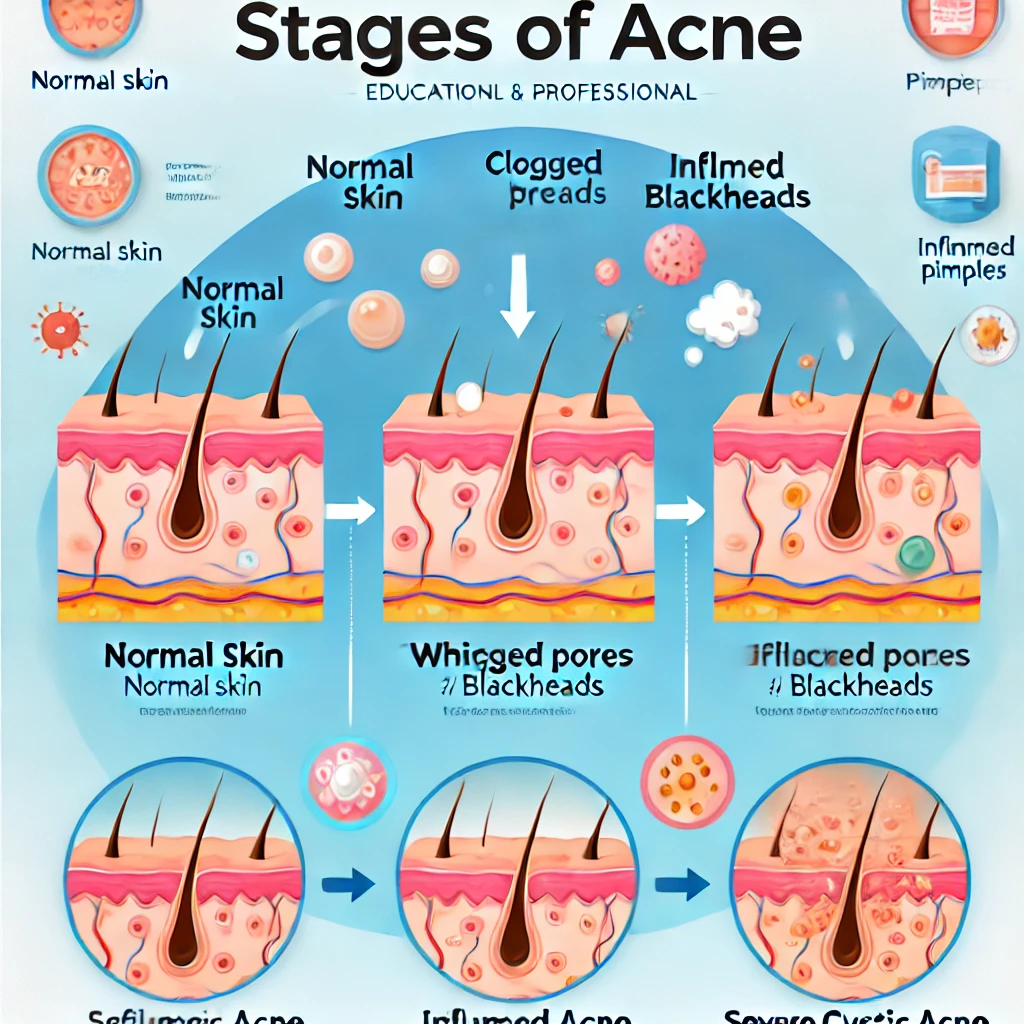
Acne occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil (sebum) and dead skin cells. This can lead to inflammation, redness, and breakouts that may range from mild to severe.
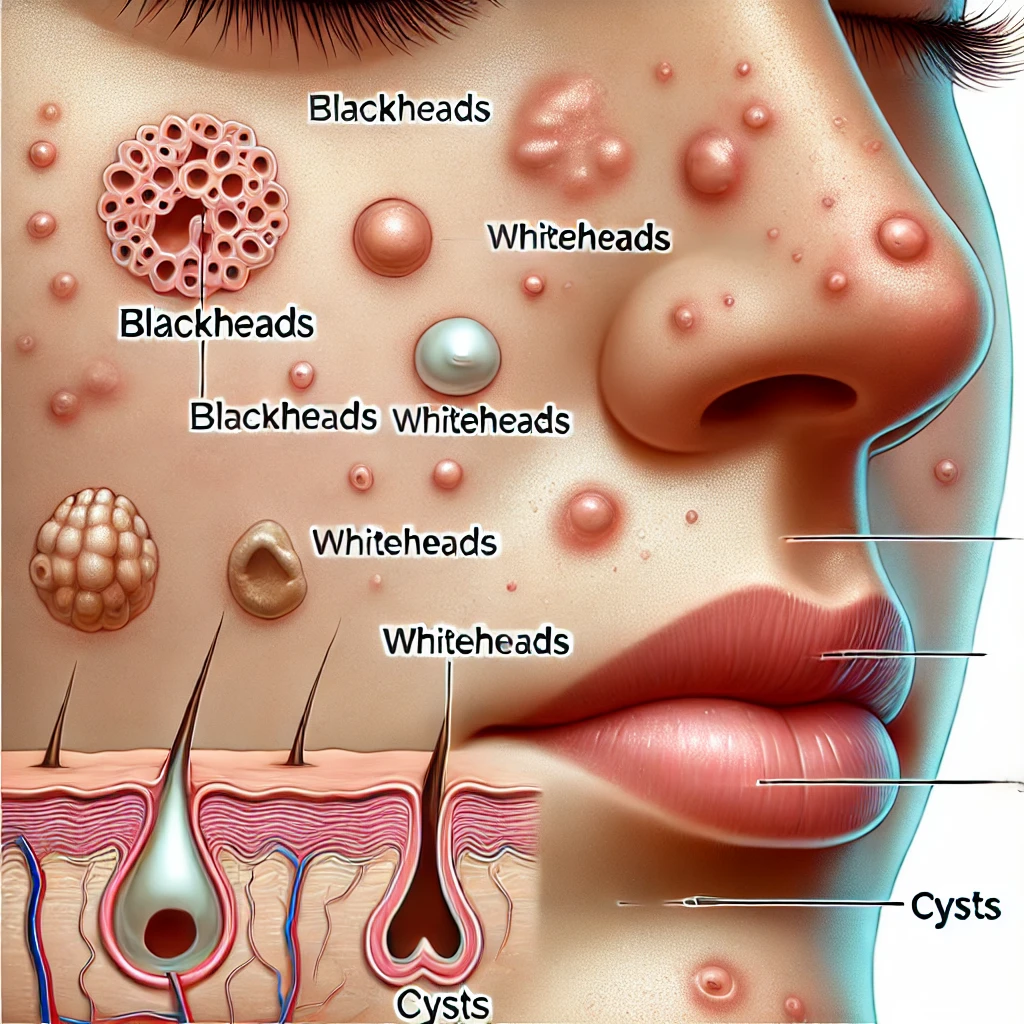
Common Causes of Acne
- Excess Sebum Production:
- Overactive sebaceous glands can produce too much oil, leading to clogged pores.
- Hormonal Changes:
- Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or menstrual cycles can trigger breakouts.

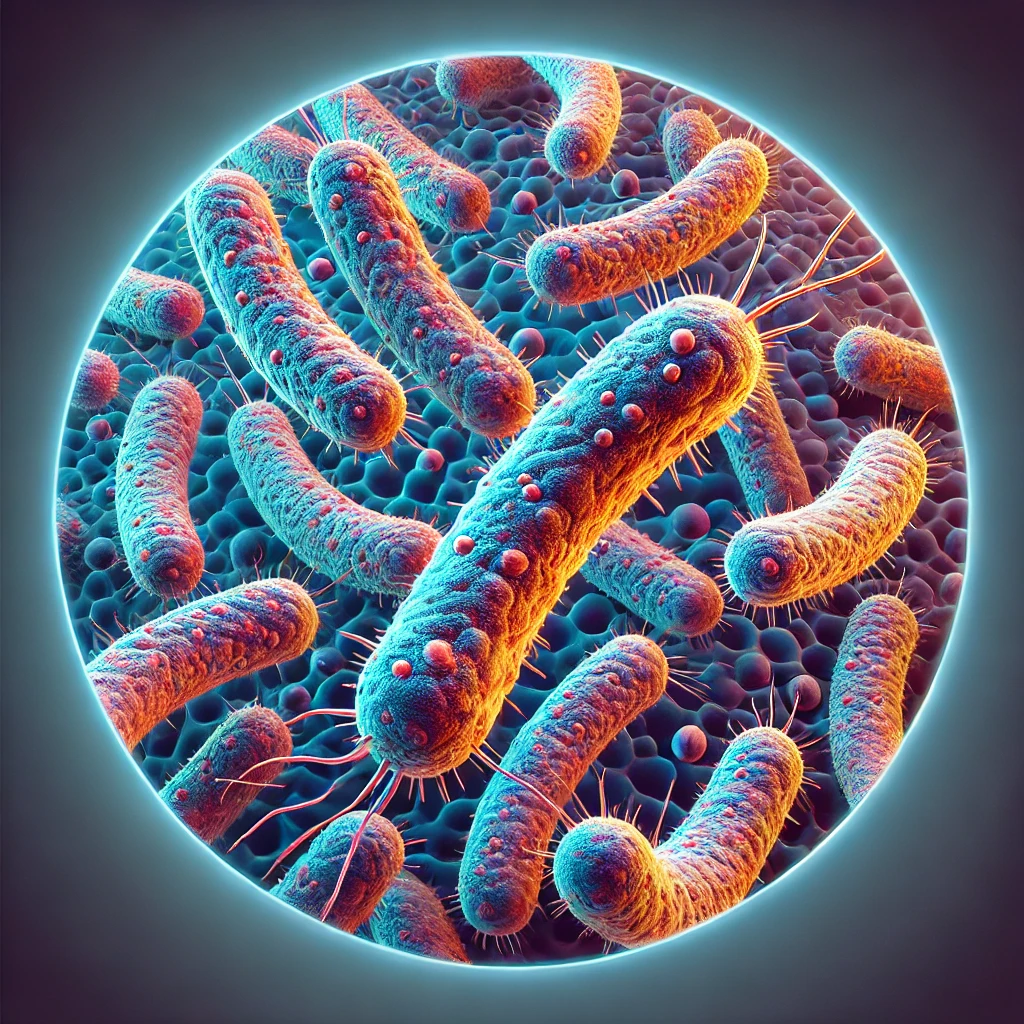
- Bacterial Growth:
- The presence of Propionibacterium acnes bacteria in the skin can exacerbate acne.
- Diet:
- High-glycemic-index foods and dairy products may contribute to acne flare-ups.

- Stress:
- Increased stress levels can worsen acne due to the body’s hormonal response.

- Cosmetic Products:
- Certain non-comedogenic products can clog pores, leading to breakouts.

- Genetics:
- A family history of acne can increase one’s likelihood of developing it.

Symptoms of Acne
- Whiteheads and blackheads
- Papules (small red bumps)
- Pustules (pimples containing pus)
- Nodules (painful, solid lumps under the skin)
- Cystic lesions (large, pus-filled lumps)
Treatment Methods
1. Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
- Benzoyl Peroxide:
- Kills acne-causing bacteria and reduces inflammation.

- Salicylic Acid:
- Helps exfoliate the skin and unclog pores.

- Retinoids:
- Promote cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.

2. Prescription Medications
- Topical Antibiotics:
- Reduce bacteria and inflammation.

- Oral Medications:
- Antibiotics: Target bacterial infection.
- Isotretinoin: Treats severe acne. (Insert image of prescription isotretinoin pills)
- Hormonal Treatments:
- Birth control pills or anti-androgens for hormone-related acne.
3. Dermatological Procedures
- Chemical Peels:
- Exfoliate the skin and reduce acne

- Laser Therapy:
- Targets bacteria and reduces oil production.
- Extraction:
- Manual removal of blackheads and whiteheads by a professional.
4. Home Remedies
- Aloe Vera:
- Soothes inflammation and promotes healing.

- Tea Tree Oil:
- Natural antibacterial properties.

Prevention Tips
- Maintain a Skincare Routine:
- Cleanse twice daily with a gentle cleanser.

- Use Non-Comedogenic Products:
- Choose skincare and makeup that won’t clog pores.

- Avoid Touching Your Face:
- Prevents the transfer of bacteria and dirt.

- Protect Skin from Sun Damage:
- Use oil-free, broad-spectrum sunscreen.

- Healthy Lifestyle:
- Exercise regularly, stay hydrated, and maintain a balanced diet.

When to See a Dermatologist
- If acne persists despite OTC treatments.
- For severe acne causing scarring.
- If you experience psychological distress due to acne.

Conclusion
Acne is a manageable condition with the right approach and consistent care. By understanding its causes and exploring various treatment options, individuals can achieve healthier skin and improved confidence. For persistent or severe cases, consulting a dermatologist can provide tailored solutions for long-term relief.